Guidelines for troubleshooting BitLocker
This article addresses common issues in BitLocker and provides guidelines to troubleshoot these issues. This article also provides pointers to start the troubleshooting process, including what data to collect and what settings to check in order to narrow down the location in which these issues occur.
Review the event logs
Open Event Viewer and review the following logs under Applications and Services logs\Microsoft\Windows:
- BitLocker-API. Review the Management log, the Operational log, and any other logs that are generated in this folder. The default logs have the following unique names:
- Microsoft-Windows-BitLocker/BitLocker Operational
- Microsoft-Windows-BitLocker/BitLocker Management
- BitLocker-DrivePreparationTool. Review the Admin log, the **Operational log, and any other logs that are generated in this folder. The default logs have the following unique names:
- Microsoft-Windows-BitLocker-DrivePreparationTool/Operational
- Microsoft-Windows-BitLocker-DrivePreparationTool/Admin
Additionally, review the Windows logs\System log for events that were produced by the TCM and TCM-WMI event sources.
To filter and display or export logs, you can use the wevtutil.exe command-line tool or the Get-WinEvent cmdlet.
For example, to use wevtutil to export the contents of the Operational log from the BitLocker-API folder to a text file that is named BitLockerAPIOpsLog.txt, open a Command Prompt window, and run a command that resembles the following:
cmd
wevtutil qe "Microsoft-Windows-BitLocker/BitLocker Operational" /f:text > BitLockerAPIOpsLog.txt
To use the Get-WinEvent cmdlet to export the same log to a comma-separated text file, open a Windows Powershell window and run a command that resembles the following:
ps
Get-WinEvent -logname "Microsoft-Windows-BitLocker/BitLocker Operational" | Export-Csv -Path Bitlocker-Operational.csv
You can use Get-WinEvent in an elevated PowerShell window to display filtered information from the System or Application log by using syntax that resembles the following:
- To display BitLocker-related information:ps
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{LogName='System'} | Where-Object -Property Message -Match 'BitLocker' | flThe output of such a command resembles the following.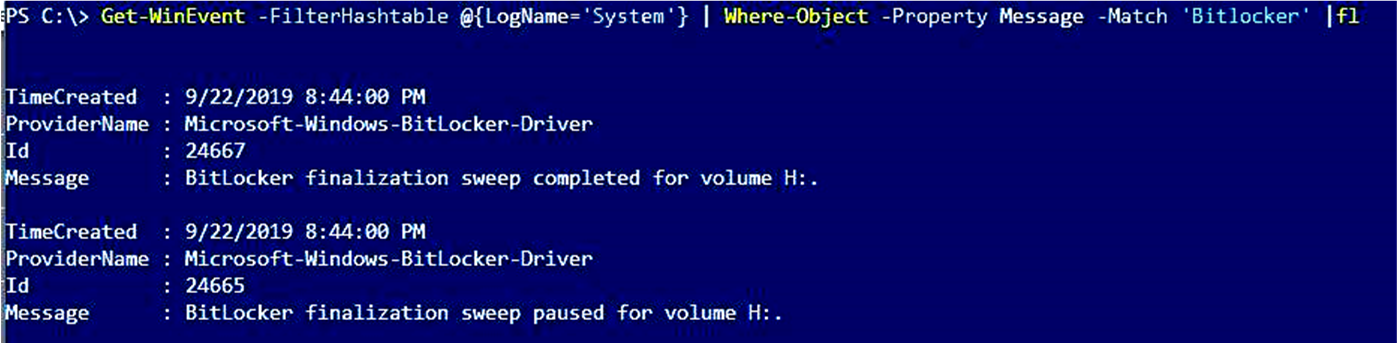
- To export BitLocker-related information:ps
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{LogName='System'} | Where-Object -Property Message -Match 'BitLocker' | Export-Csv -Path System-BitLocker.csv - To display TPM-related information:ps
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{LogName='System'} | Where-Object -Property Message -Match 'TPM' | fl - To export TPM-related information:ps
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{LogName='System'} | Where-Object -Property Message -Match 'TPM' | Export-Csv -Path System-TPM.csvThe output of such a command resembles the following.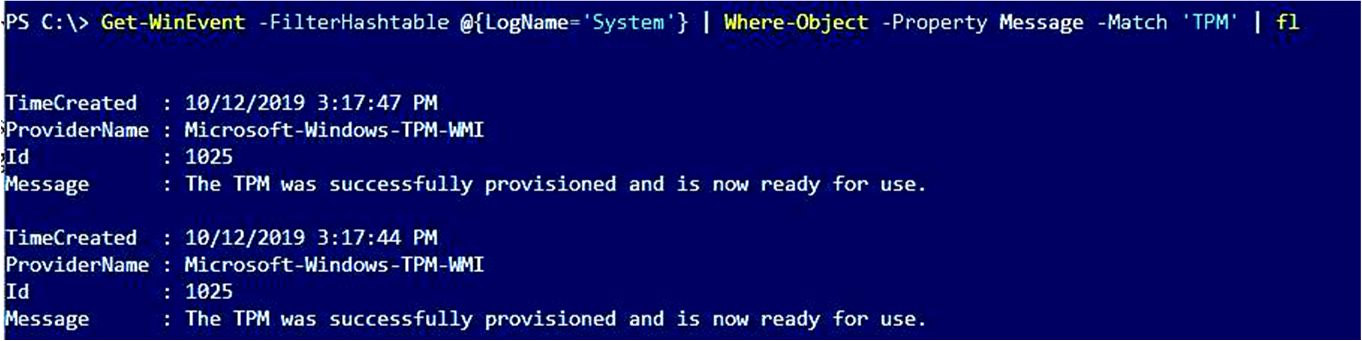
Note
If you intend to contact Microsoft Support, we recommend that you export the logs listed in this section.
Gather status information from the BitLocker technologies
Open an elevated Windows PowerShell window, and run each of the following commands.
Review the configuration information
- Open an elevated Command Prompt window, and run the following commands.
- Open Registry Editor, and export the entries in the following subkeys:
- HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\FVE
- HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\TPM\
Check the BitLocker prerequisites
Common settings that can cause issues for BitLocker include the following:
- The TPM must be unlocked. You can check the output of the get-tpm command for the status of the TPM.
- Windows RE must be enabled. You can check the output of the reagentc command for the status of WindowsRE.
- The system reserved partition must use the correct format.
- On Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) computers, the system reserved partition must be formatted as FAT32.
- On legacy computers, the system reserved partition must be formatted as NTFS.
- If the device that you are troubleshooting is a slate or tablet PC, use https://gpsearch.azurewebsites.net/#8153 to verify the status of the Enable use of BitLocker authentication requiring preboot keyboard input on slates option.
For more information about the BitLocker prerequisites, see BitLocker basic deployment: Using BitLocker to encrypt volumes
Next steps
If the information that you have examined so far indicates a specific issue (for example, WindowsRE is not enabled), the issue may have a straightforward fix.
Resolving issues that do not have obvious causes depends on exactly which components are involved and what behavior you see. The information that you have gathered can help you narrow down the areas to investigate.
- If you are working on a device that is managed by Microsoft Intune, see Enforcing BitLocker policies by using Intune: known issues.
- If BitLocker does not start or cannot encrypt a drive and you notice errors or events that are related to the TPM, see BitLocker cannot encrypt a drive: known TPM issues.
- If BitLocker does not start or cannot encrypt a drive, see BitLocker cannot encrypt a drive: known issues.
- If BitLocker Network Unlock does not behave as expected, see BitLocker Network Unlock: known issues.
- If BitLocker does not behave as expected when you recover an encrypted drive, or if you did not expect BitLocker to recover the drive, see BitLocker recovery: known issues.
- If BitLocker does not behave as expected or the encrypted drive does not behave as expected, and you notice errors or events that are related to the TPM, see BitLocker and TPM: other known issues.
- If BitLocker does not behave as expected or the encrypted drive does not behave as expected, see BitLocker configuration: known issues.
We recommend that you keep the information that you have gathered handy in case you decide to contact Microsoft Support for help to resolve your issue.

0 comments: